M Cm Mm Km Chart
marihuanalabs
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
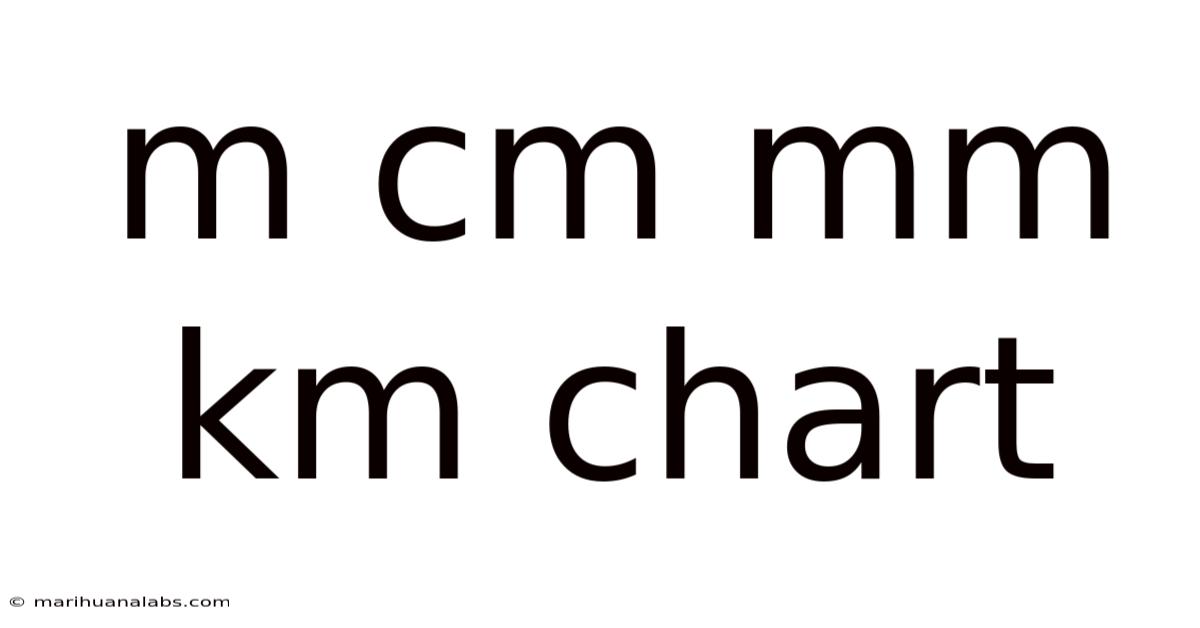
Table of Contents
Understanding Metric Conversions: A Comprehensive Guide to the m cm mm km Chart
Understanding metric conversions, specifically the relationships between meters (m), centimeters (cm), millimeters (mm), and kilometers (km), is crucial for anyone working with measurements in science, engineering, construction, or everyday life. This comprehensive guide will provide a clear understanding of these units, their conversions, and practical applications, using a visual chart and detailed explanations. We'll delve into the practical uses of each unit, clear up common confusions, and offer real-world examples to solidify your understanding. This resource aims to be your definitive guide to mastering metric conversions.
Introduction to the Metric System
The metric system, officially known as the International System of Units (SI), is a decimal system based on powers of 10. This means that converting between units involves simply multiplying or dividing by factors of 10, making it incredibly straightforward compared to other systems like the imperial system. The core unit of length in the metric system is the meter (m). All other units of length, including centimeters (cm), millimeters (mm), and kilometers (km), are derived from the meter. This makes it simple to visualize and calculate relationships.
The m cm mm km Chart: A Visual Representation
The following chart visually represents the relationships between meters, centimeters, millimeters, and kilometers:
| Unit | Abbreviation | Relationship to Meter (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Kilometer | km | 1 km = 1000 m |
| Meter | m | 1 m = 1 m |
| Centimeter | cm | 1 m = 100 cm |
| Millimeter | mm | 1 m = 1000 mm |
This chart provides a quick reference for understanding the relative sizes of each unit. Remember, the metric system is based on powers of 10, making conversions a matter of simply moving the decimal point.
Detailed Explanation of Each Unit
Let's examine each unit in more detail:
-
Kilometer (km): This is the largest unit of length commonly used in the chart. Kilometers are used to measure large distances, such as the distance between cities, the length of a road trip, or the altitude of a mountain. One kilometer is equal to 1000 meters.
-
Meter (m): The meter is the base unit of length in the metric system. It's a commonly used unit for measuring everyday objects, such as the height of a person, the width of a room, or the length of a piece of furniture.
-
Centimeter (cm): Centimeters are smaller than meters, used for measuring smaller objects. One meter is equal to 100 centimeters. Think of measuring the length of a pencil, the width of a book, or the height of a plant.
-
Millimeter (mm): Millimeters are the smallest unit of length commonly used in this context. They are used for measuring very small objects or precise measurements. One meter is equal to 1000 millimeters. Examples include the thickness of a wire, the diameter of a screw, or the size of an insect.
Conversion Calculations: Step-by-Step Examples
Understanding how to convert between these units is crucial. Here are some step-by-step examples:
Example 1: Converting kilometers to meters:
Let's say you have a distance of 5 kilometers (km) and you need to convert it to meters (m). Since 1 km = 1000 m, you simply multiply the number of kilometers by 1000:
5 km * 1000 m/km = 5000 m
Therefore, 5 kilometers is equal to 5000 meters.
Example 2: Converting meters to centimeters:
Imagine you have a length of 2.5 meters (m) and need to convert it to centimeters (cm). Knowing that 1 m = 100 cm, you multiply the number of meters by 100:
2.5 m * 100 cm/m = 250 cm
Thus, 2.5 meters is equal to 250 centimeters.
Example 3: Converting centimeters to millimeters:
Suppose you have a measurement of 15 centimeters (cm) and want to convert it to millimeters (mm). Remember that 1 cm = 10 mm:
15 cm * 10 mm/cm = 150 mm
Therefore, 15 centimeters is equivalent to 150 millimeters.
Example 4: Converting millimeters to meters:
You have a tiny object measuring 350 millimeters (mm) and need to express its length in meters (m). Since 1 m = 1000 mm, you divide the number of millimeters by 1000:
350 mm / 1000 mm/m = 0.35 m
So, 350 millimeters is equal to 0.35 meters.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The m cm mm km chart and its conversions find applications in numerous fields:
- Construction: Measuring building materials, land plots, and distances within a construction site.
- Engineering: Designing and constructing machines, bridges, and other structures requires precise measurements.
- Manufacturing: Producing parts and components with precise dimensions.
- Cartography: Creating maps and representing distances on a scale.
- Everyday Life: Measuring furniture, clothing sizes, and distances for everyday tasks.
Let's look at some real-world examples:
- A map might show a distance of 25 km between two cities. You can easily convert this to meters (25,000 m) if needed for more detailed calculations.
- A tailor might measure the length of a piece of fabric in centimeters. This allows for precise cutting and fitting.
- An engineer might specify the diameter of a pipe in millimeters to ensure a perfect fit in a complex system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the easiest way to remember the conversions between these units?
A: Remember the base unit is the meter (m). Kilometers are bigger (1000 times bigger), centimeters are smaller (1/100th), and millimeters are even smaller (1/1000th). Visualizing the chart and practicing conversions will reinforce your memory.
Q: Can I use a calculator for these conversions?
A: Absolutely! Calculators are helpful for quick conversions, especially with larger or more complex numbers. However, understanding the underlying principles is still essential.
Q: Are there other units of length in the metric system?
A: Yes, there are other units, such as micrometers (µm) and nanometers (nm), used for extremely small measurements. However, the m, cm, mm, and km are the most commonly used in daily life and many professional applications.
Q: What if I need to convert between metric and imperial units (inches, feet, miles)?
A: Conversion factors exist for this. You can use online converters or consult conversion tables for accurate results. However, understanding metric conversions is a crucial first step.
Conclusion
Mastering the metric system, particularly the relationships between meters, centimeters, millimeters, and kilometers, is a valuable skill with far-reaching applications. This guide, coupled with the provided m cm mm km chart and practical examples, offers a strong foundation for understanding and confidently using metric conversions in various contexts. Consistent practice and applying these conversions in real-world scenarios will further enhance your understanding and proficiency. Remember to visualize the relative sizes of these units to make the conversions more intuitive. With consistent practice, you'll quickly become comfortable working with these essential units of measurement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Xbox 360 Halo Combat Evolved
Sep 12, 2025
-
Country Apple Fritter Bread Recipe
Sep 12, 2025
-
Hair Salon Guildford Mall Surrey
Sep 12, 2025
-
Chihuahua Puppies For Sale Ontario
Sep 12, 2025
-
Temperature For A Ball Python
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about M Cm Mm Km Chart . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.